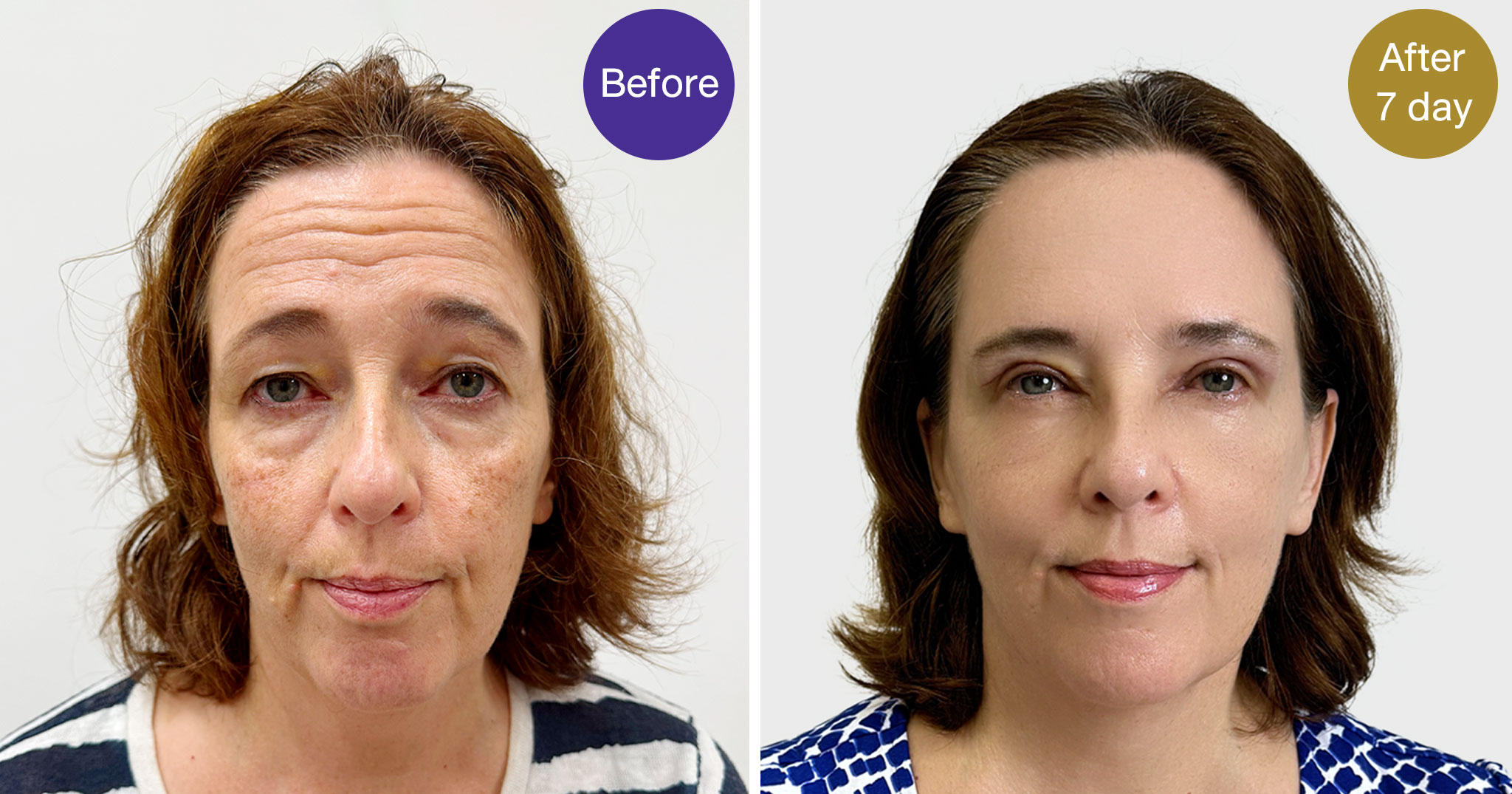
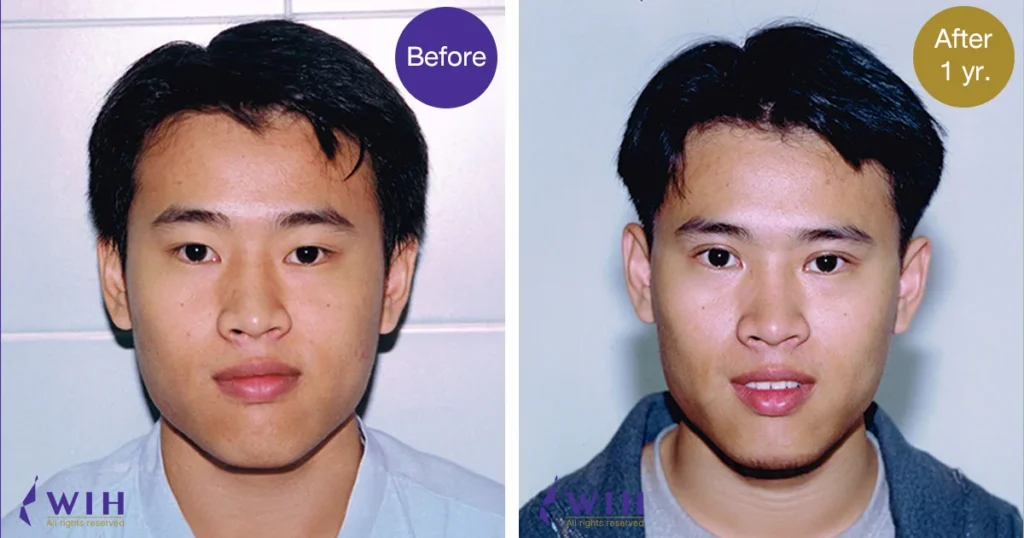
Rejuvenate your eyes at WIH Hospital with expert Blepharoplasty, including Double Eyelid surgery. Address droopy eyelids, under-eye bags, and vision concerns. Learn about upper/lower eyelid surgery, ptosis correction, and sub-brow lifts. Schedule your consultation today for a refreshed look.
What is Eyelid Surgery (Blepharoplasty)?
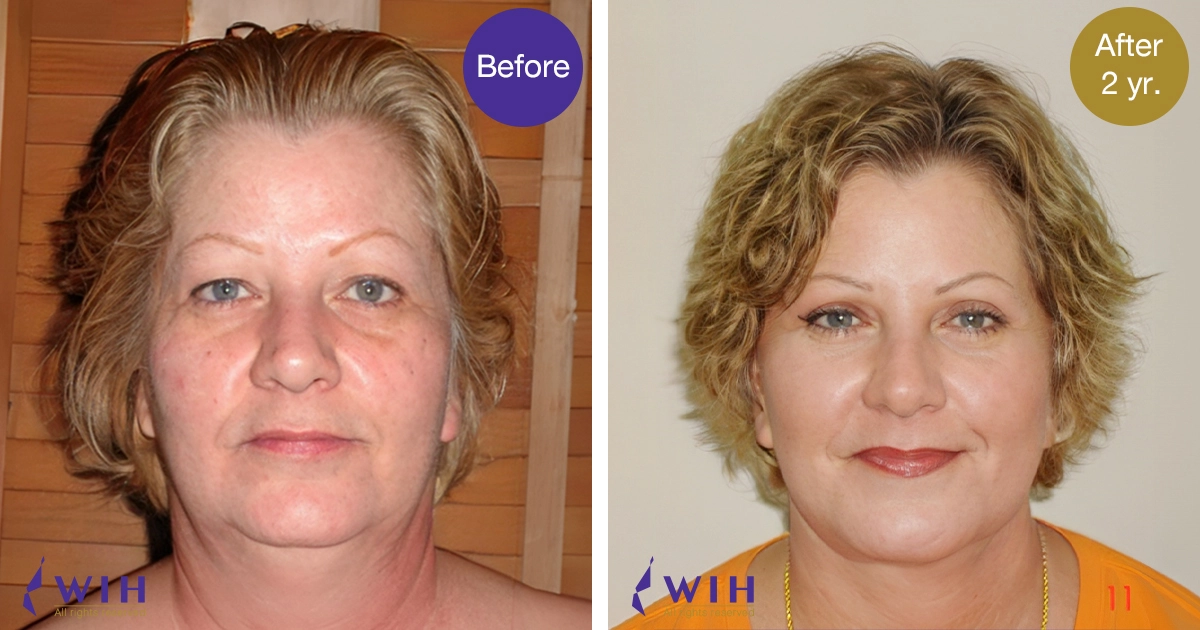
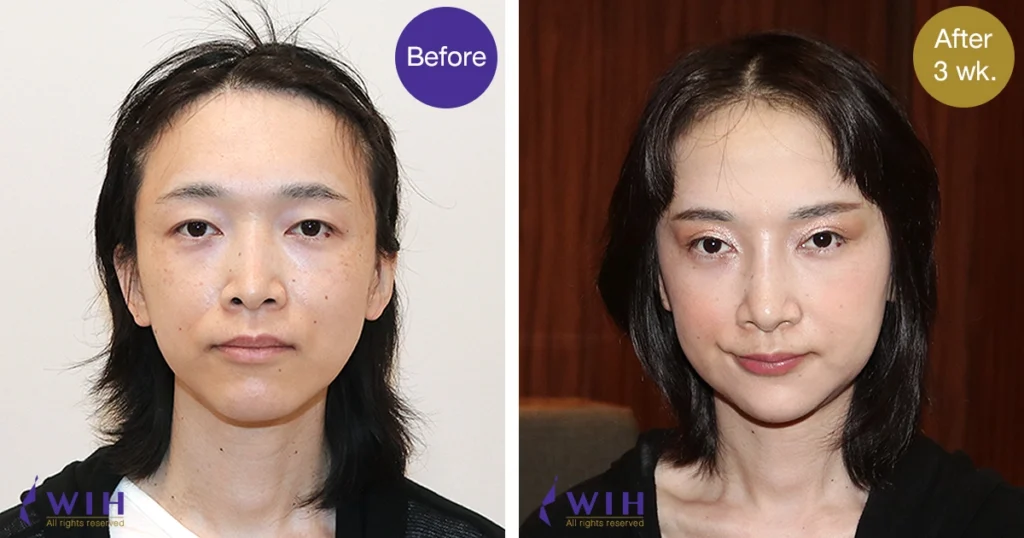
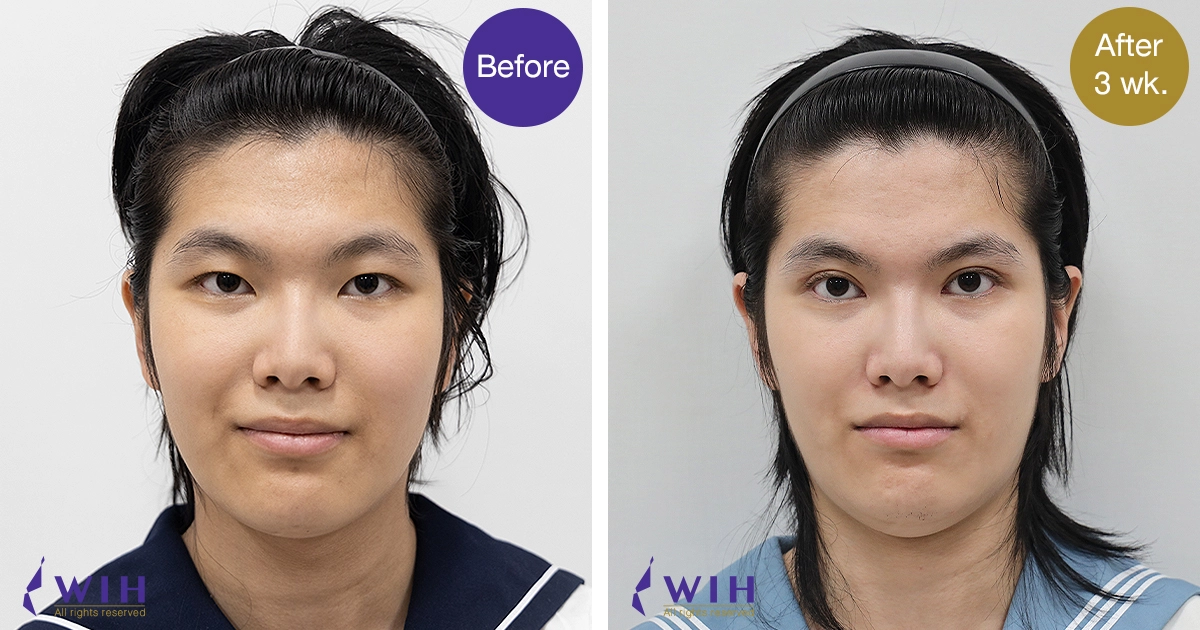
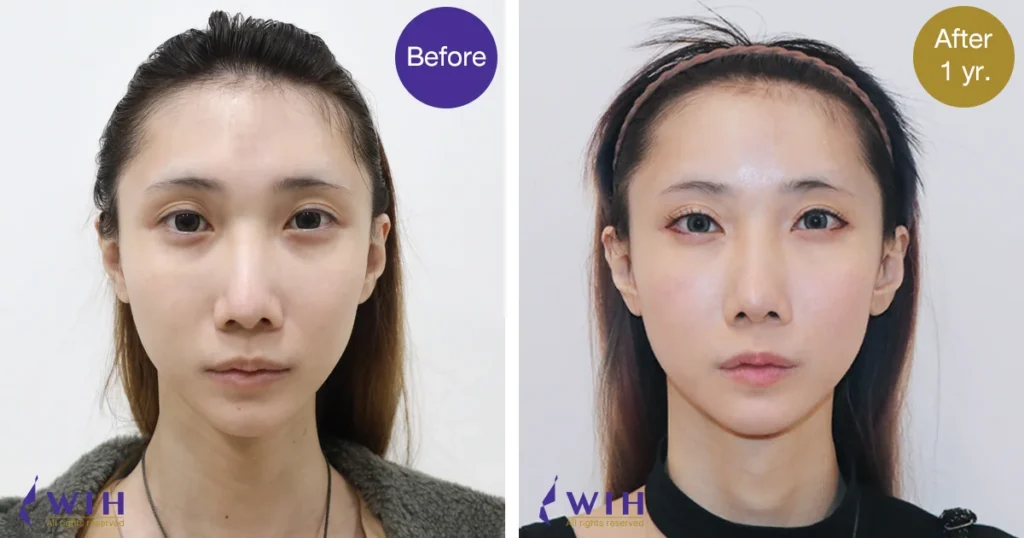
Eyelid Surgery, commonly known as Blepharoplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to improve the appearance of the eyelids and, in some cases, address functional issues like obstructed vision. Its target excess skin, fat, and muscle around the eyes, which can lead to a tired, aged, or even visually impaired appearance.
Upper Eyelid Surgery (Upper Blepharoplasty)
Upper eyelid surgery, or upper blepharoplasty, is a cosmetic procedure designed to remove excess skin, fat, and in some cases, muscle from the upper eyelids. For many Asian individuals, this surgery is commonly performed to create a natural-looking double eyelid crease.
Lower Eyelid Surgery (Lower Blepharoplasty)
Lower eyelid surgery is a procedure to address concerns below the eye, such as under-eye bags, puffiness, fine lines, and sagging skin, to remove the excess fat for skin tightening.
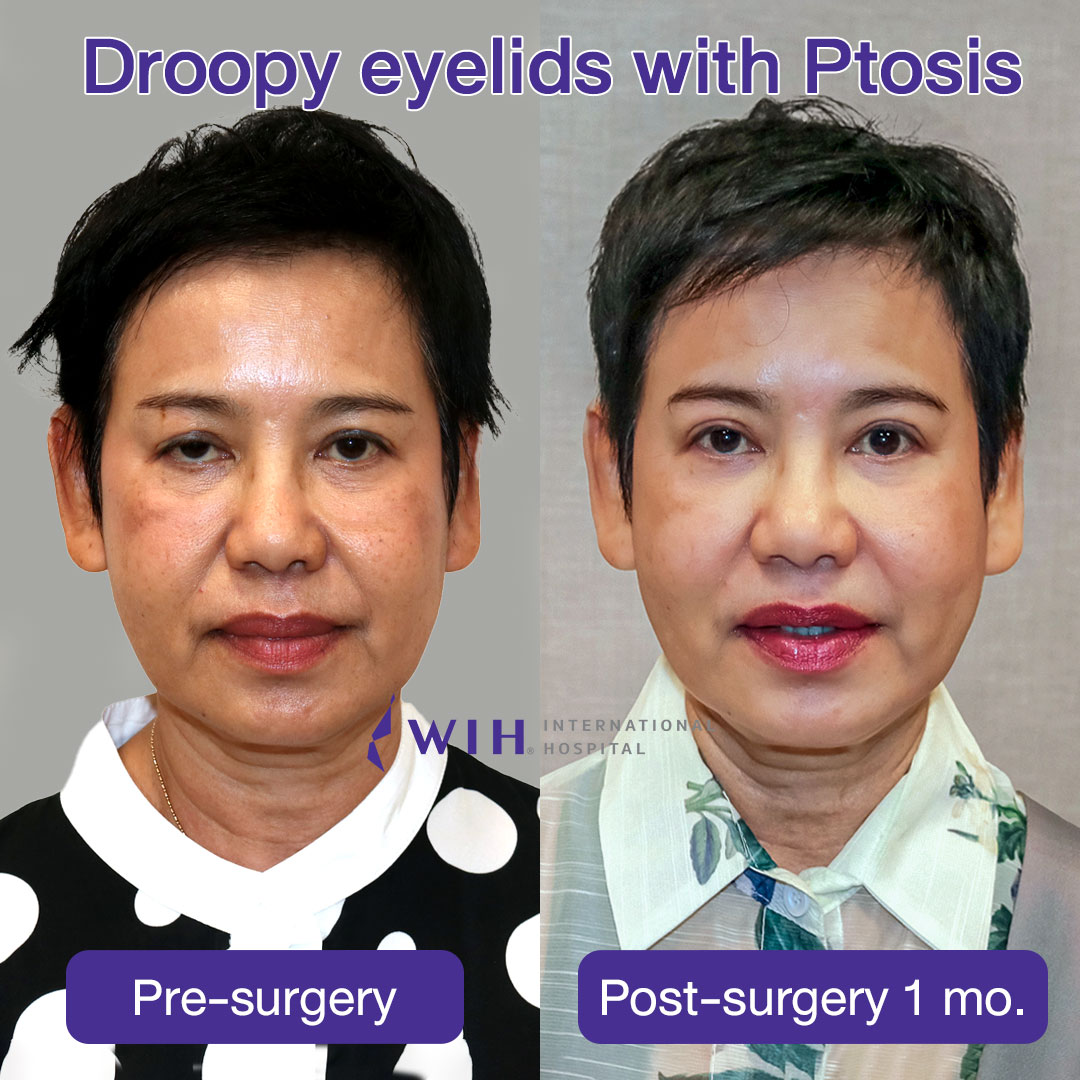
Ptosis Correction (Correction of Drooping Eyelids)
Ptosis is a medical condition characterized by the drooping of the upper eyelid, often due to weakened levator muscles. Ptosis correction surgery aims to lift the eyelid to its proper position, restoring full vision and improving aesthetic symmetry.
Sub-Brow Lift
Sub-brow lift is a technique where an incision is made below the eyebrow to remove excess skin and muscle, effectively lifting the outer portion of the upper eyelid and eyebrow.
High Fold Technique (Asian Blepharoplasty)
The High Fold technique, a form of Asian Blepharoplasty, aims to create a higher and more pronounced double eyelid crease. This method is customized to the unique anatomical features of Asian eyelids, and the removal of skin and fat improves eye size and shape to achieve a more dramatic and well-defined crease.
Epicanthoplasty
Epicanthoplasty is a surgical procedure designed to remove or modify the epicanthal fold, which is the skin fold covering the inner corner of the eye. This procedure can make the eyes appear larger and wider.
A Good Candidate for Eyelid Surgery
- Sagging skin on the upper or lower eyelids
- Puffiness or under-eye bags
- Drooping upper eyelids
- Brow sagging
- Impaired vision due to eyelid issues
Comprehensive Consultation
- The consultation will include a thorough assessment of the eye area, a discussion of aesthetic goals, reviewing medical history, and a detailed explanation of the recommended procedure.
- Eyelid surgery procedures are typically performed under local anesthesia or with sedation. But it can vary depending on the procedure.

Pre-Operative and Post-Operative Care Eyelid Surgeries
Pre-operative Care
- Follow all medication guidelines provided by your surgeon.
- Abstain from smoking and alcohol as instructed.
- Adhere to fasting instructions.
Post-operative Care
- Our dedicated nursing staff will monitor you in our recovery area. You will be provided with specific post-operative instructions.
- Small dressings will be applied to the incision sites.
- The surgeon will prescribe Eye drops or ointments.
- Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will be scheduled to monitor your healing progress.
Recovery Timeline
- Week 1: Stitches are typically removed (if applicable), and vision may be slightly blurry.
- Weeks 2-3: Bruising and swelling largely subside. Incision lines will begin to fade but may still be pink. Makeup can usually be applied. Most can return to work and light exercise.
- Weeks 4-6: The eyes look increasingly natural and refreshed.
- Months 3-6 (Final Result): The incision lines are nearly invisible. The final results become apparent.
Potential Risks
- Temporary blurred or double vision
- Dry eyes
- Difficulty closing eyes completely
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
Benefits
- Youthful and refreshed appearance
- Reduction of the signs of aging around the eyes
- Improved Vision
- Enhanced Confidence
- Long-Lasting Results
Patient Testimonial
ดูโพสต์นี้บน Instagram
Before & After Surgery Gallery
FAQ
Typically 1 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity and whether upper, lower, or both eyelids are addressed.
Incisions are strategically placed in natural creases or inside the eyelid, making scars minimal and usually fading to be nearly invisible.
The results are generally long-lasting, often for many years.
Upper eyelid surgery primarily removes excess skin or fat for cosmetic improvement. Ptosis correction specifically targets the weakened levator muscle, causing the eyelid to droop and obstruct vision, a functional concern.
High Fold technique creates a higher and more pronounced double eyelid crease, tailored to the unique anatomy of Asian eyelids for a more dramatic effect.
Epicanthoplasty modifies or removes the epicanthal fold at the inner corner of the eye, making the eyes appear wider and larger.
At WIH Hospital, your journey to rejuvenated eyes is guided by highly skilled, board-certified surgeons who possess extensive expertise in eyelid aesthetics with world-class facilities and a deeply patient-centric approach, ensuring personalized care from your initial consultation through to your complete recovery. Our commitment lies in achieving natural, aesthetically pleasing results that truly enhance your unique facial harmony.