At WIH International Hospital, this surgery is performed by Dr. Chettasak Tulayaphanich—formerly known as Dr. Chettawut—a highly experienced surgeon with over 30 years of expertise in gender-affirming surgery. He has developed and refined a unique technique called Dr. Chet’s NPI (Non-Penile Inversion) Technique.
Concept Behind Dr. Chet’s NPI Skin Graft Vaginoplasty
Unlike the traditional Penile Inversion Technique, which rolls penile skin inward to create the vaginal canal (often resulting in insufficient depth or poor aesthetic outcome in patients with small genitalia or prior circumcision), Dr. Chettasak’s NPI technique preserves the penile skin for crafting delicate and natural-looking external genital structures, such as the labia minora and vaginal introitus.
Skin Graft Vaginoplasty in this approach uses only scrotal skin (Total Scrotal Skin Graft), which is trimmed and thinned to an ideal thickness (approximately 0.3–0.45 mm) to form the entire neovaginal lining.
If the scrotal skin is insufficient after designing the outer labia (labia majora), Dr. Chettasak may harvest additional skin from the groin area. This site is chosen over more distant areas such as the lower abdomen or inner thighs to avoid large or visible scars.
Surgical Steps (1–7)
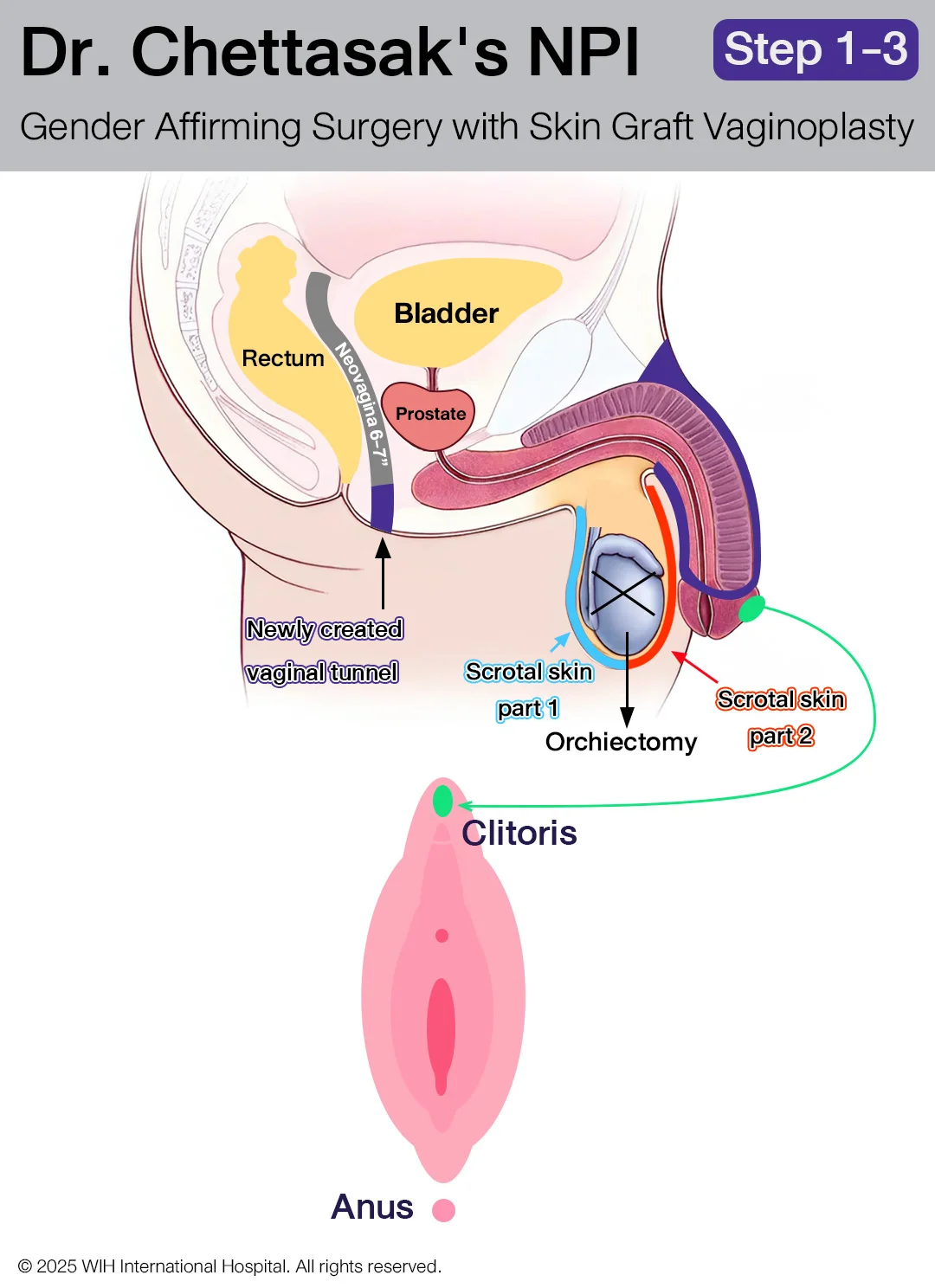
Step 1: Creating the Vaginal Opening and Canal
The vaginal opening is placed about 2–3 cm above the anus. Dissection is carefully performed along the anterior wall of the rectum, creating a tunnel between the rectum and urinary system—starting from the urethra, through the prostate, to the bladder. The vaginal canal is created to a depth of at least 6 inches, even in patients with small genitalia or prior circumcision.
Step 2: Bilateral Orchiectomy
The testicles and spermatic cords (including the vas deferens) are removed as close to the inguinal ring as possible to ensure a smooth contour without any palpable remnants in the groin.
Step 3: Creating the Clitoris, Clitoral Hood, and Frenulum
The clitoris is sculpted to a proportionate feminine size and accurately positioned along the vulva axis. The clitoral hood and frenulum are carefully constructed to enhance both aesthetics and sensitivity. Sensory nerve branches from the pudendal nerve are preserved and well-innervate not only the clitoris but also the hood, frenulum, and the sensitive area just below the clitoris. This nerve-preserving approach—unique to the NPI technique—supports orgasmic potential and long-term sexual function.
Step 4: Penectomy and Urethral Shortening
The penis is removed, while preserving the penile skin for later use in reconstructing external genital structures. The urethral opening is repositioned just above the vaginal opening, mirroring cis-female anatomy. Surrounding corpus spongiosum (spongy tissue) is meticulously removed to prevent residual tissue lumps that may become engorged during sexual arousal. This ensures a smooth, natural-looking urethral meatus.
Step 5: Constructing the Labia Minora and Vaginal Introitus
Dr. Chettasak uses the inner prepuce and upper penile skin to form the labia minora, shaping a delicate pink inner lining. The lower penile skin is vertically aligned to form the introitus and posterior fourchette with a realistic V-shaped opening.
Step 6: Creating the Outer Labia (Labia Majora Reconstruction)
The scrotal skin is carefully divided into two portions.
The first portion is sculpted to form the labia majora (outer labia). Dr. Chettasak meticulously designs this area to achieve a natural, full contour that resembles the appearance of natal female anatomy.
Step 7: Graft Preparation and Vaginal Lining Insertion
The second portion of the scrotal skin is prepared into an intermediate-thickness skin graft, typically between 0.3–0.45 mm. This preserves the dermis layer, making the graft strong, resilient to friction, and free of hair follicles, which reduces the risk of internal hair growth in the neovagina.
Hair root remnants, if detected during graft preparation, can be carefully removed by scraping with a scalpel to prevent future hair regrowth.
The prepared skin graft is then sutured into a tube-like pouch around a custom vaginal mold, with the dermis layer facing outward (toward the vaginal canal).
This graft-lined mold is inserted into the previously created vaginal canal, and sterile gauze packing is added to:
- Maintain canal width and depth
- Promote proper graft adherence to the wound bed
This internal support remains until the graft successfully attaches and vascularizes, ensuring optimal healing and long-term durability of the neovaginal lining.
Skin Graft Vaginoplasty Compared to Colon and PPV: Pros & Considerations
Skin graft vaginoplasty offers a safe and less invasive alternative to colon and peritoneal vaginoplasty (PPV). While colon vaginoplasty provides natural lubrication and slightly longer depth, it involves abdominal surgery with higher surgical risks. PPV avoids bowel use but requires laparoscopy and may limit depth in some patients.
In most cases, skin graft vaginoplasty using total scrotal skin can achieve vaginal depth comparable to PPV and nearly equal to colon vaginoplasty, without abdominal incisions. It is also more cost-effective and ideal for patients seeking a balanced approach between aesthetics, function, and recovery.
How Is a Skin Graft Neovagina Different from a Natural Vagina?
Important Precautions for Long-Term Comfort and Safety
A neovagina constructed using the Skin Graft Vaginoplasty technique, such as in Dr. Chettasak Tulayaphanich’s signature NPI (Non-Penile Inversion) method, differs from a natal (cisgender) vagina in several essential ways:
1. Lack of Natural Lubrication
Unlike the vaginal mucosa in cisgender women or the intestinal lining used in colon vaginoplasty, skin grafts do not contain mucus-secreting glands. This means that skin graft neovaginas cannot self-lubricate.
Recommendation: Use a generous amount of water-based lubricant during every instance of vaginal dilation and sexual penetration.
2. Thinner and More Sensitive Tissue
The grafted skin is carefully trimmed to a thickness of 0.3–0.45 mm to prevent hair follicle inclusion. This makes the tissue thinner and more delicate than normal skin, and more prone to frictional damage, especially within the first year after surgery.
3. Common Area for Friction-Related Injuries
The first 2–3 inches inside the vaginal opening is the most vulnerable zone. Without adequate lubrication, this area may develop abrasions, erosions, or granulation tissue, particularly during dilation or intercourse.
Lubrication Guidelines for Skin Graft Neovagina
To maintain the health, function, and comfort of your neovagina:
- Always use water-based lubricants, with a focus on coating the vaginal entrance and the first few inches inside.
- During the first 3 months after surgery, it is safest to use your finger to insert the lubricant deeply into the neovagina. Fingers allow precise control of direction and pressure, reducing the risk of trauma to the graft.
- Avoid using gel applicators unless specifically advised by your surgeon. Incorrect use may cause scratching or graft irritation.
For more information, see our full guide on Vaginal Dilation Care
FAQ
Yes. Dr. Chettasak’s technique does not rely on penile skin for depth, making prior circumcision irrelevant. Scrotal skin can sufficiently achieve full depth.
Yes. It avoids abdominal incisions and bowel involvement, resulting in faster, safer recovery.
No. The graft is precisely trimmed to eliminate hair follicles and inspected thoroughly before implantation.
A graft thinner than 0.3 mm is prone to shrinkage, poor resistance to friction, and may tear easily. A full-thickness graft is hard to take, risks graft loss, and may contain hair follicles, leading to unwanted hair growth.
The graft goes through a 3-stage process:
- Stage 1: Plasma Imbibition (Day 1–2) – the graft absorbs plasma from the wound bed
- Stage 2: Inosculation & Microvascularization (Day 3–5) – new blood vessels start connecting
- Stage 3: Full Revascularization (Day 5–7) – the graft is securely integrated
By Day 6–7, gauze can be removed, and vaginal dilation (“dilator training”) can safely begin.